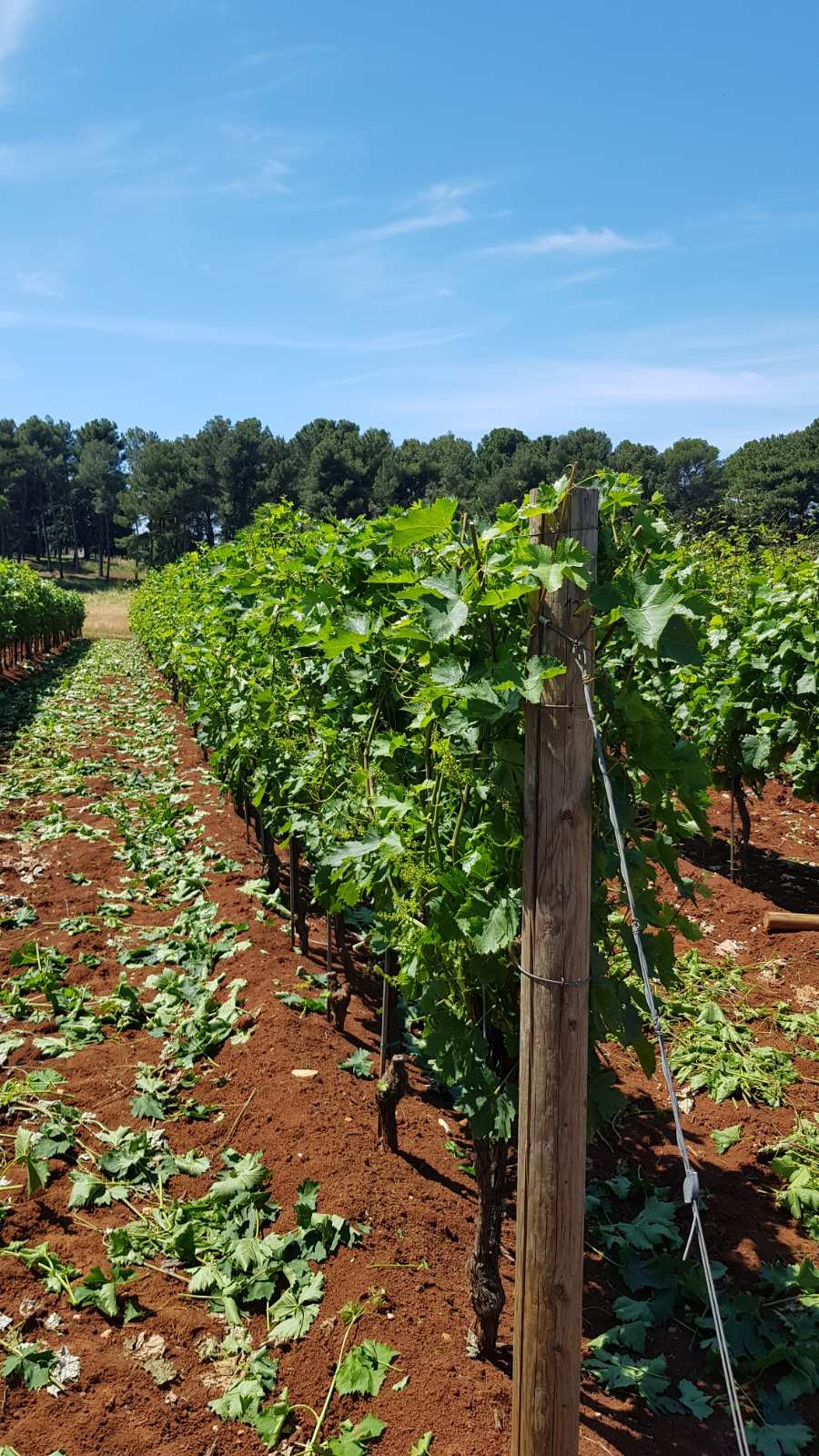
After winter dormancy buds start to swell and shoots start to sprout on the vine.
It looks like nothing needs to be done but this part of the growth cycle is crucial to how your vine is going to look and what kind of grapes you will get.
In this text, we will explain which jobs need to be done and how to do them properly.
Vine cleaning
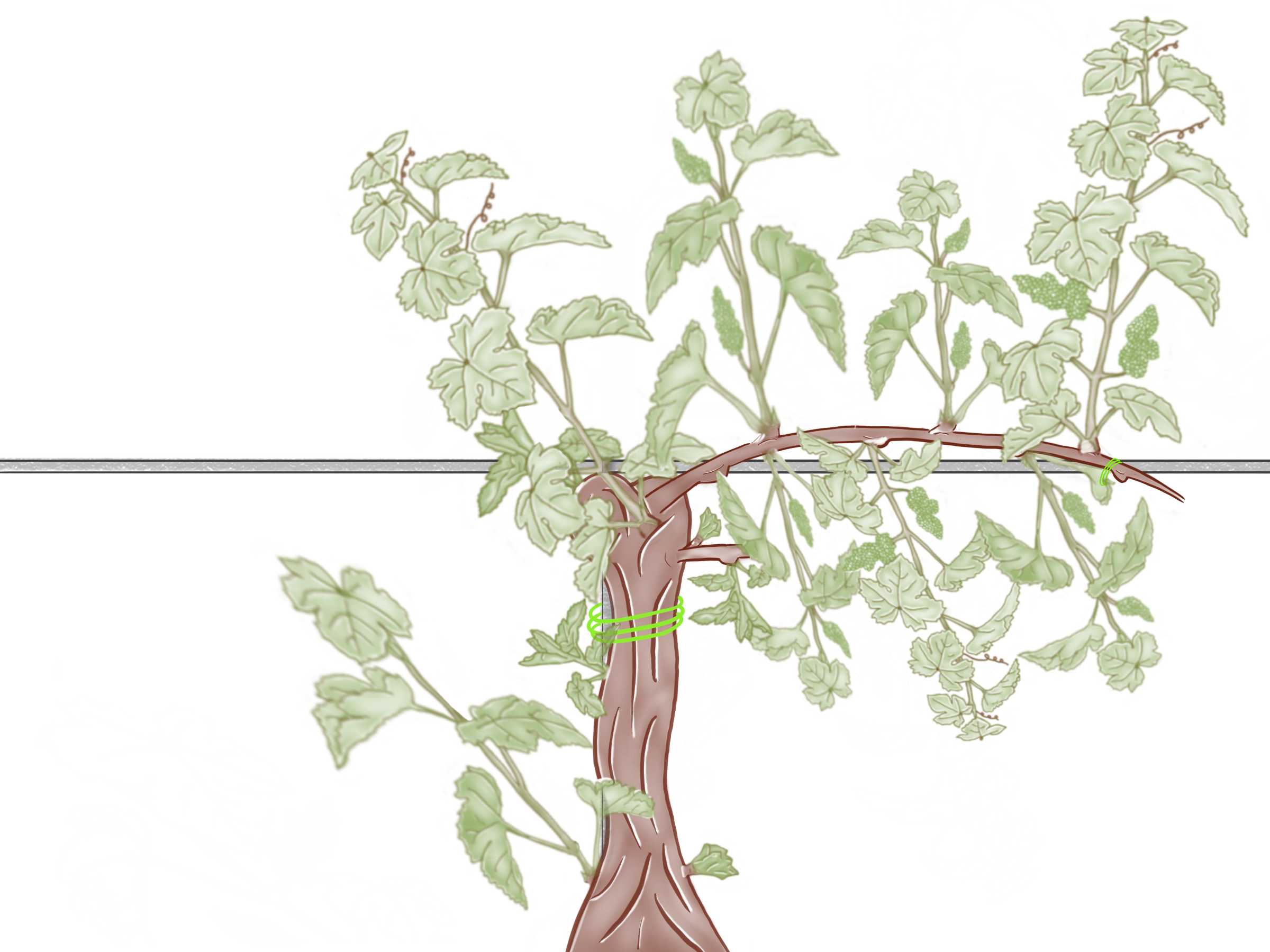
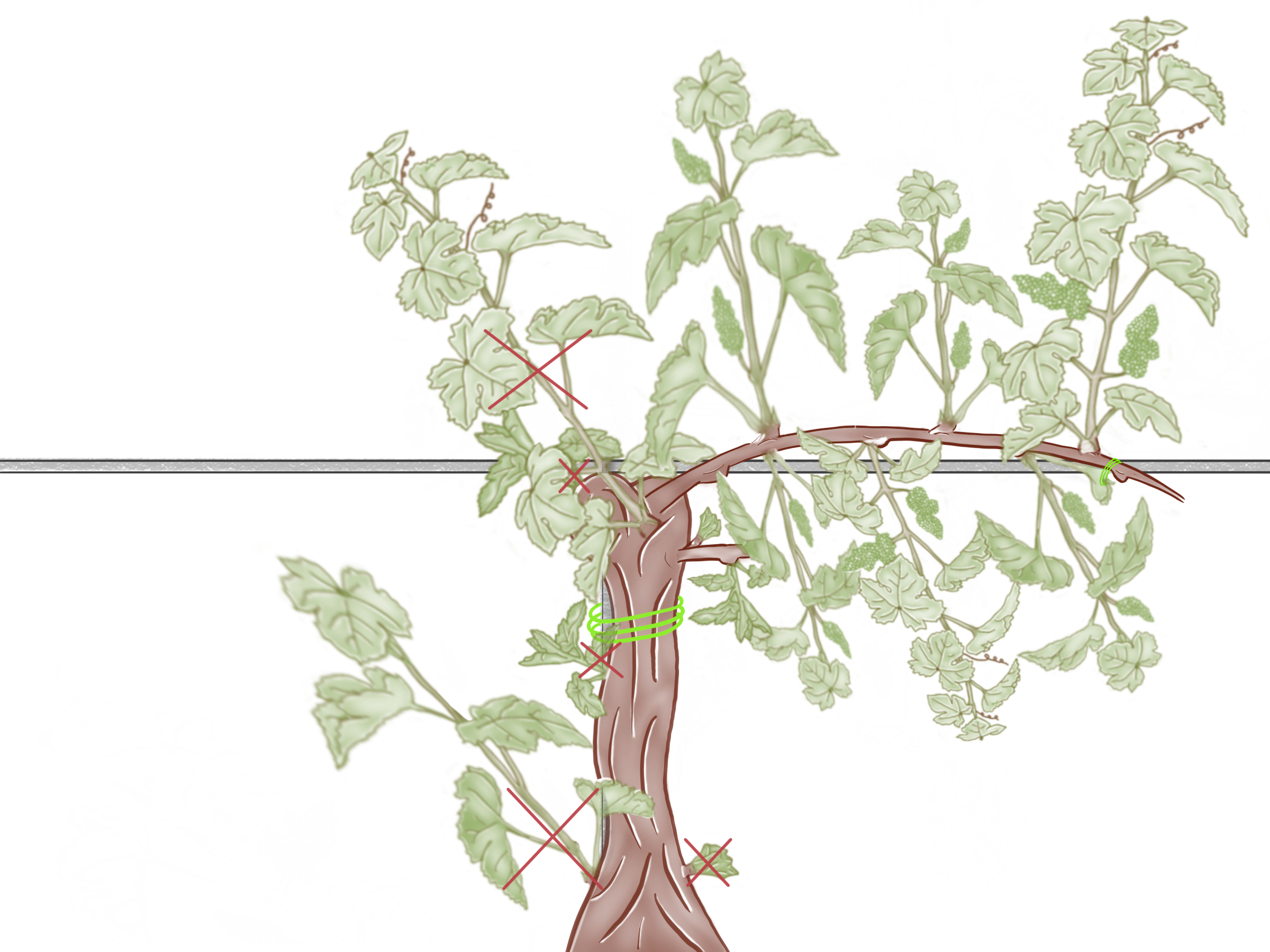
At the beginning of the first growth cycle, you need to clean the old wood from shoots that sprouted from the sleeping buds.
We do it because all the shoots that sprout from sleeping buds won’t give any grapes, we need to remove them because we want all the food to go to the fertile shoots.
Why it is done in the growth phase?
It is done in this phase because the shoots are still green and young and you can just break them easily without using shears.
In that way, you don’t leave wounds and scars.
Scars are the passage for fungal diseases.
Vine thinning
If you want to keep your vine healthy you need to make room for air to pass through it and we need to keep it thin so we don’t get brushwood.
Usually, it is done when the shoot is 15-30cm long but we can do it while we clean the vine.
The difference is that when the shoots are bigger it is easier to recognize the fertile shoots.
We remove less developed shoots, if 2 shoots come from the same bud we leave the more developed ones.
To get high-quality grapes u leave 8-12 shoots per meter of vine length because if you leave more they would make shade to each other.
Also, after thinning inside the vine processes start to occur and compensate for the losses(cut parts), the rest of the shoots that we left get stronger and develop better.
Vine tips trimming
Tips trimming is cutting the tips of the shoots with the youngest leaves.
It is done 2 times in vegetation or 3 times if in a rainy season comes to the high development of shoots.
After the first trimming high development starts so we need a second trimming but if the climate is dry there will be no high development.
How and when to trimm your vines?
Trimming is done a few days after fertilization and flower growth, the second trimming is done 3 weeks after the first one and the third trimming is done in case of a rainy day and high development of shoots.
With trimming, we shape the green surface of the vine so it has 110-140heith and 30-40 width.
Trimming can be done in the phenophases 12-31
Goals of trimming
- Lower the volume of space that a shoot is going to take.
- Improve the microclimate inside the vine (especially in the zone of the grapes)
- Determination of the final look of your vine throughout the vegetation
- Influence on the level of fertilization
Effects of trimming
If it is done during the flowering stage it can elevate the degree of fertilization.
When the growing tips which are using the assimilate are cut an amount is left for the development of flowers that jet has to get Fertil.
There are negative effects and they occur if the vine is cut while grapes are ripening.
Vine partial defoliation
Partial defoliation(leaf removal) is done in the grapes zone (around the grapes).
Usually, only a part of the leaves is removed so that the grape zone remains partly shaded.
If you are producing wine the type of wine determines the level of defoliation.
- Sparkling wine – no defoliation
- Fresh wines (especially white) – gentle defoliation
- Structured/full wines(especially red) – more intense defoliation
- Dessert wine – intense defoliation especially in later stages so that grapes can ripen fully
Vine grapes thinning
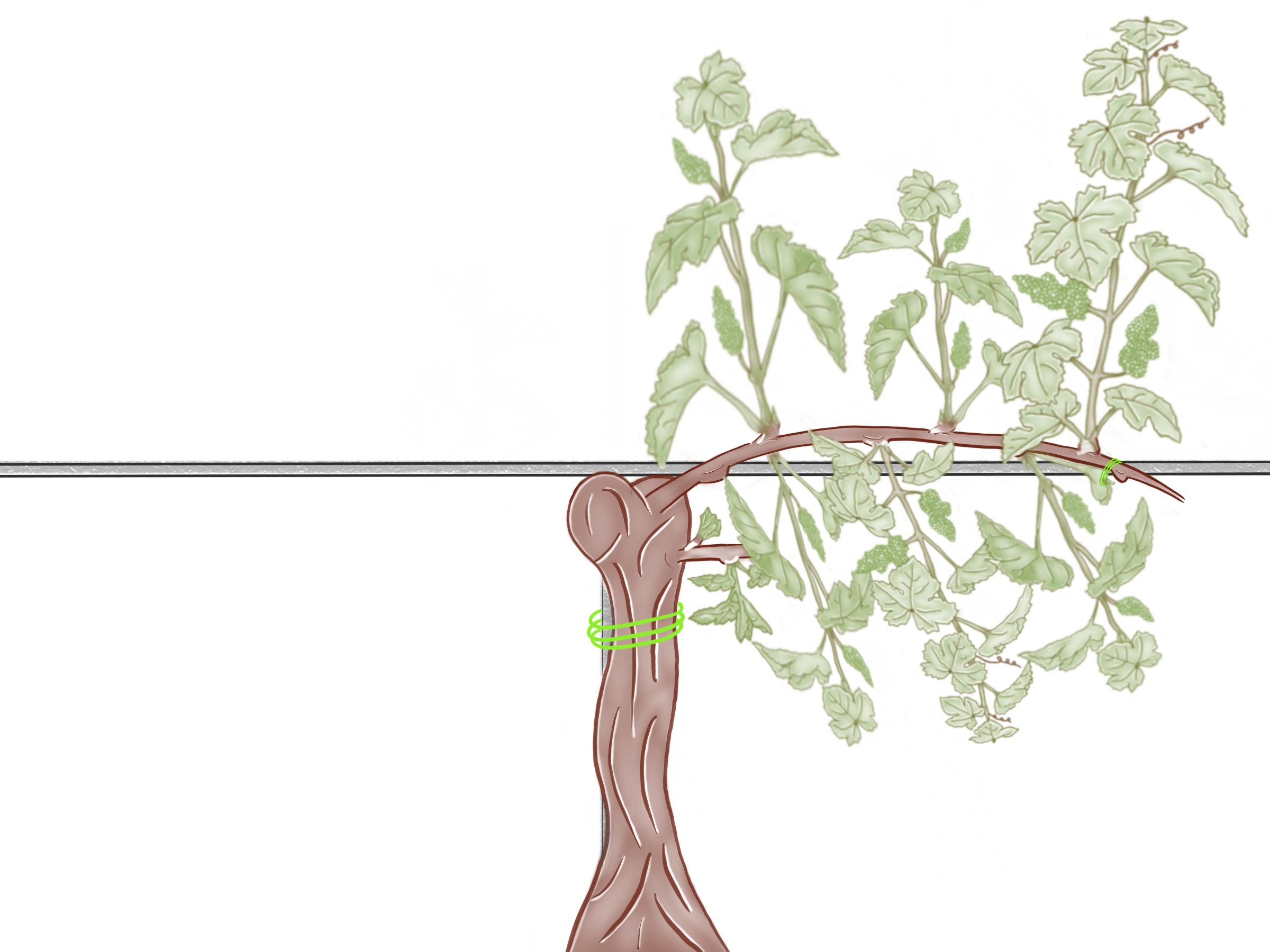
Final look of the vine
Before
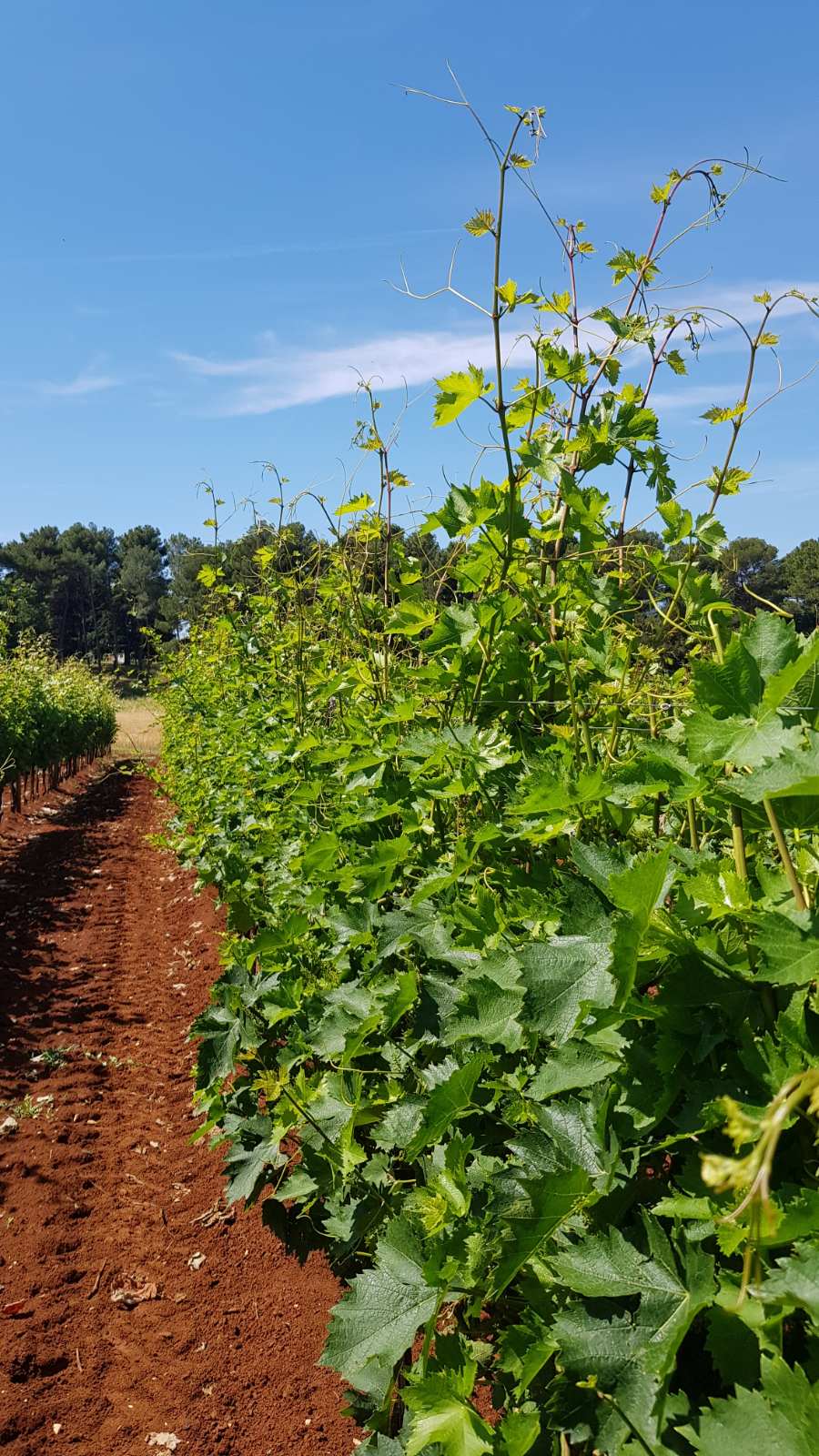

After
